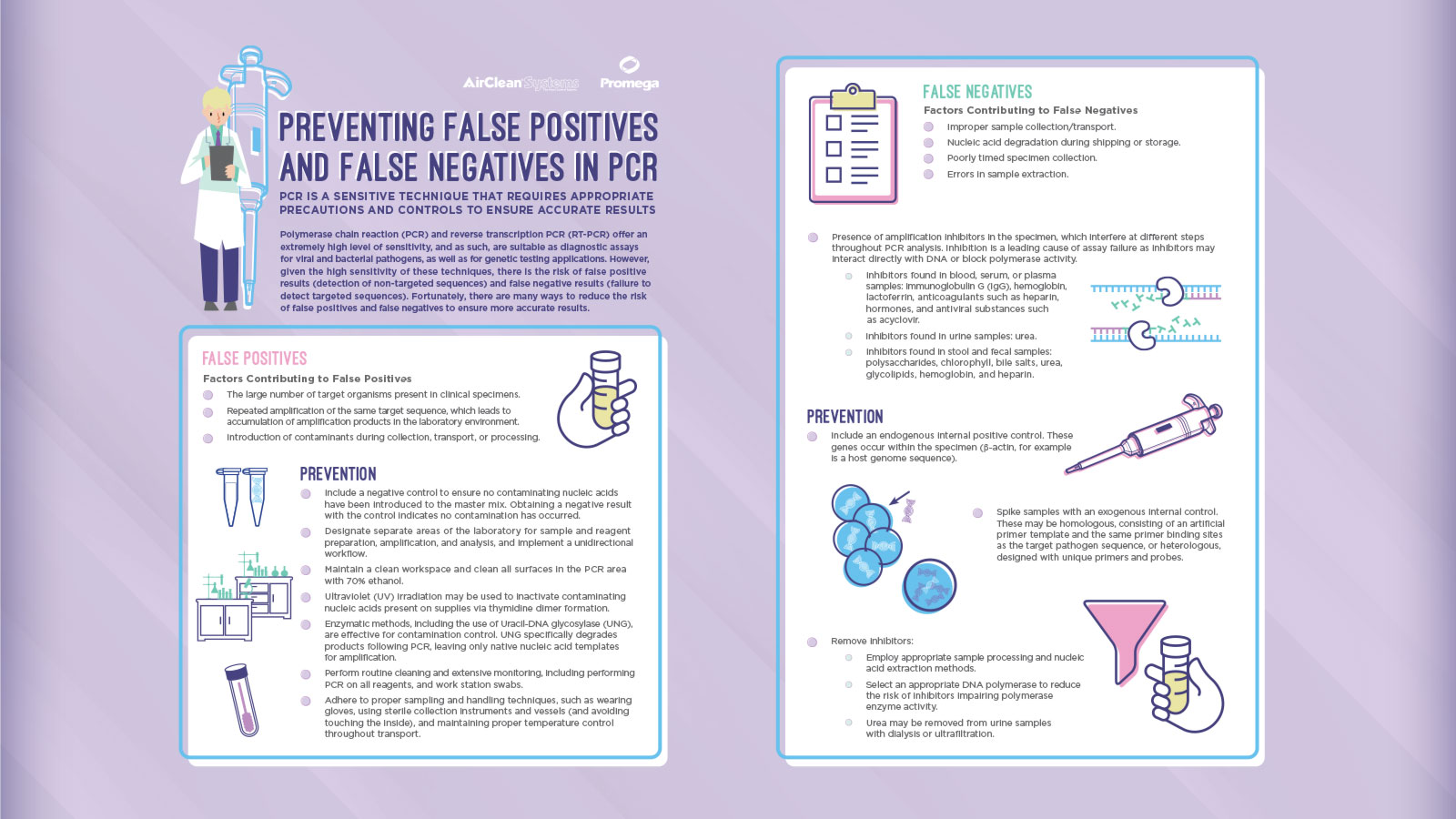
Preventing False Positives and False Negatives in PCR
Learn about what contributes to false positives and false negatives and how to prevent them

Published:May 01, 2020
|1 min read
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) offer an extremely high level of sensitivity, and as such, are suitable as diagnostic assays for viral and bacterial pathogens, as well as for genetic testing applications. However, given the high sensitivity of these techniques, there is the risk of false positive results (detection of non-targeted sequences) and false negative results (failure to detected targeted sequences). Fortunately, there are many ways to reduce the risk of false positives and false negatives to ensure more accurate results.
Download the FREE infographic courtesy of Clinical Lab Manager.